Overview¶
Objective¶
When setting up an IoT eco-system with a lot of different devices, it becomes quickly problematic to have them talking to each other smoothly. There are a number of choices to make in order for this to happen. This project assumes that some of those choices have been made: using MQTT as the messaging transport. What this project does is helping in the next set of choices to make: choosing a consistent messaging model and defining its implementation via a MQTT syntax.
If all the devices involved already communicate via MQTT, this project can only help with its proposed syntax for MQTT messages. If some devices can’t communicate natively via MQTT, then this project proposes a python wrapper that should facilitate writing the gateway between these devices and the MQTT network. This gateway can then run as a service on a machine that is connected to these devices via whatever interface is available: serial, bluetooth, TCP, or else.
Concepts¶
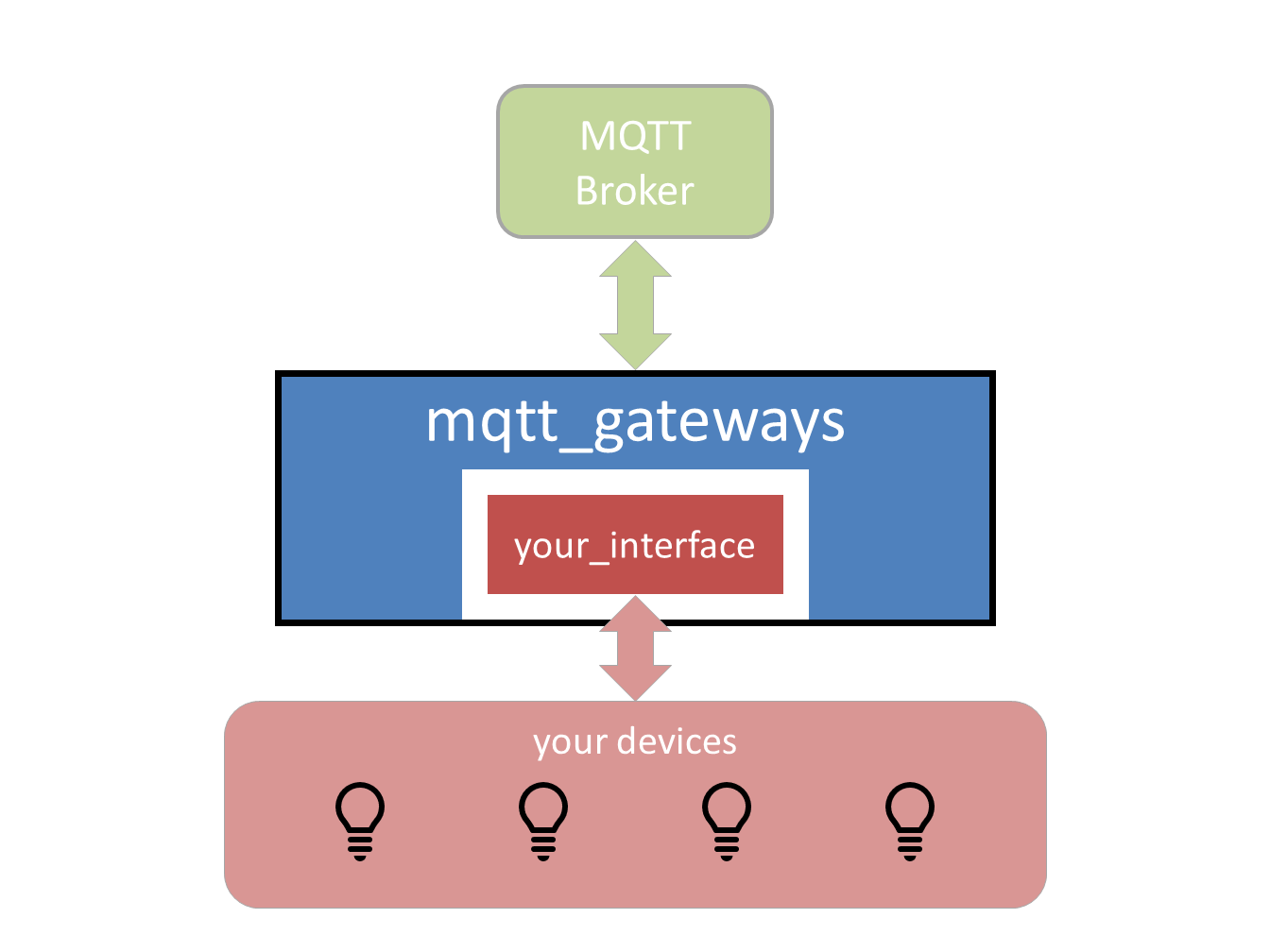
This project has 2 parts:
- The definition of the messaging model: the project has its own model for messages which is adapted to domestic IoT environments. It is an abstraction layer that defines a message by many attributes and not only by destination and content.
- The implementation of this model through a python wrapper to communicate via MQTT networks. The wrapper takes care of the addressing syntax and the commands translation via mapping data provided by the interface.
For a more in-depth information, go to Concepts.
Usage¶
This project is provided with the core application (the wrapper), and an example interface (the dummy interface) that does not interface with anything but shows how the system works. The developer can then write its own interface by using the dummy interface as a template. There are also some already developped interfaces available in the repository.
Installation¶
The installation involves a copy of the repository and the setting of some configuration parameters. The only dependency is the paho.mqtt library.
For the full installation guide, go to Installation.
Develop your interface¶
The interface is made of a class that has to define the 2
methods __init__ (to initialise the interface) and loop
(called periodically to do whatever needs to be done to interact
with the devices), very much like an Arduino script setup and loop functions.
The loop method communicates with the application via 2 lists of
messages (an incoming and an outgoing one). It reads the incoming list
for commands from the MQTT environment and writes into the outgoing list any
updates on status or commands sent from the devices to the rest of the network.
In the most classic example, a serial interface is the only way to communicate with
the device. The __init__ method would initialise the serial port and the
loop method would write to the serial port any command received from the
application through the incoming message list, and read the serial port
for messages from the device to be forwarded to the application.
If needed, a mapping JSON file can store the correspondence between the MQTT keywords and the internal keywords. This feature is available in case the MQTT syntax needs to change.
For a complete guide on how to develop an interface, go to Tutorial.
For a more detailed description of the project, go to Project Description.